
Using the gross margin commission model gets your sales team thinking about the most important KPI in your business, profit margins. As a result, their focus shifts from total revenue to the bottom line. So, your people will concentrate on selling the kinds of jobs to the types of clients that truly earn them (and the business) the most money – those that generate the strongest profit margins. A tiered commission structure is a compensation model where sales professionals earn commissions at varying rates depending on the volume of sales they achieve. Instead of a flat percentage, this structure rewards higher sales with increasing commission rates, creating tiers of earnings potential.
How much are you saving for retirement each month?

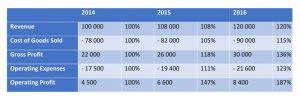
The net revenue commission is easy to use, but that’s really the only benefit it has over the gross margin commission model – how to calculate commission on net profit especially if your services aren’t set at fixed price points. Gross sales are often referred to as top-line revenue on an income statement. It is the total amount of sales generated, or that you have receipts for, during a given period. If a salesperson generated $100,000 in gross sales transactions in a given month, that means he completed transactions with that amount of revenue received.
Commission Plan Types with Industries
- A tiered commission structure is a compensation model where sales professionals earn commissions at varying rates depending on the volume of sales they achieve.
- We don’t need to tell you that your business depends on sales, and you must find ways to continuously motivate your sales force.
- When I first started researching this, it felt overwhelming, but getting the knowledge of these details showed me how really important they are for rewarding team efforts.
- This model can apply to straight commission and base salary + commission models.
- A commission plan can be simple or complex depending on the sales process and how a product is sold to an end-user.
- Additionally, companies also use more complex commission structures like a tiered commission or different commission rates for different products or services.
- It reassures them that someone handles pay and tax correctly, contributing to a positive work environment.
Overrides are additional commissions that are given to a manager or supervisor based on the performance of the sales team that they are responsible for. Whether you’re a sales manager or a sales rep, understanding the commission calculation process can help you achieve your sales goals and maximize your earnings. A commission plan can be simple or complex depending on the sales process and how a product is sold to an end-user. Here’s a comprehensive list of factors you can use to design the perfect commission scheme for your business.
Get in Touch With a Financial Advisor
Consulting with a tax accounting professional can provide tailored advice and peace of mind. They offer insights that are especially valuable for small business payroll management. Compliance with tax regulations and employment laws is non-negotiable in payroll management. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and harm to business reputation. These services manage payroll tasks, ensuring compliance and accuracy while you focus on your core business activities.

What is your current financial priority?
As a seller reaches higher sales thresholds, the commission rate escalates, often retroactively applying higher rates to all sales or incrementally to sales beyond each threshold. This incentivizes sales representatives to exceed their sales goals, as their earning potential grows alongside their performance. First off, when figuring out sales commissions, you need to choose the commission period – this is typically a month or bi-weekly span, during which sales will count towards earning commissions. Next, calculate the commission base by identifying all revenue that qualifies for commissions after excluding any ineligible earnings, like maintenance revenue or special contract terms. Once you have the base, applying the commission rate is easy – basically, multiply the base by the rate specified in the salesperson’s contract. Also, think about any factors that might adjust this rate, like bonuses for exceeding targets or different rates for all sorts of product types.
What Is the Net Revenue Commission Model?
- Whatever the arrangement, a salesperson needs to know what their likely commission is before closing a deal.
- For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
- No matter if you have one employee or many, you must follow tax and employment laws.
- Usually, the employer determines the length of the commission period, which might be anything from daily to quarterly or even annual.
- Industries such as retail, manufacturing, distribution, and wholesale often utilize profit margin commission structures to motivate sales teams and drive efficient sales practices.
- Calculating commissions with a straight commission structure is super helpful in areas with steady sales, which makes the sales funnel very easy.
- For great performers, I might even add a commission override to increase their rate as a reward for surpassing their quotas.
For example, if the commission base is $100,000 and the commission rate is 10%, the salesperson would receive a commission of $10,000. To determine the amount of commission, multiply the representative’s commission rate by the total sales made during the commission period. Gross profit commission is commission paid on the profit margin of a deal rather than the revenue. For example, if there are several components to a deal, like products and implementation services, where each has different profit margins. A commission period is the length of time – a month, a quarter, or a year – where a commission rate applies.
In the case of a tiered commission structure, adjust the rates accordingly. For instance, a $10,000 deal concluded in Q1 may receive a 10 percent bonus, raising the commission from 10 percent to 11 percent. However, if the deal finalizes in Q4, it might not qualify for any increase, and the commission would stay at the standard 10 percent bookkeeping and payroll services rate.
